The real interest in measuring the state of the insulation of a electrical machine or an installation lies in checking whether the quality of these isoltators has been altered over the years by the demanding operations.
09-09-2020
The measurement of the insulation resistance is intended to control and verify the state of this insulation once the assembly of the different elements of the transformer has been completed. The aim is to check that no errors or accidents have occurred during manufacture or assembly that could cause insulation failure. Although this phase of the insulation check is not covered by any transformer manufacturing standard, it is performed by some manufacturers to obtain information on the condition of the connections, the insulators and the grounding of the transformer core.
The real interest of measuring the state of the insulation of a machine or an installation lies in checking whether the quality of these insulators has been altered over the years by demanding operations. Fatigue of electrical, mechanical, chemical or thermal stress causes a reduction in the electrical resistivity of the insulators, which in turn leads to an increase in leakage currents that accelerate this deterioration process that will ultimately cause incidents that may affect the safety of people and things, including production stoppages in industry.
The total current flowing through an insulation subjected to a test voltage for insulation measurement is composed of:
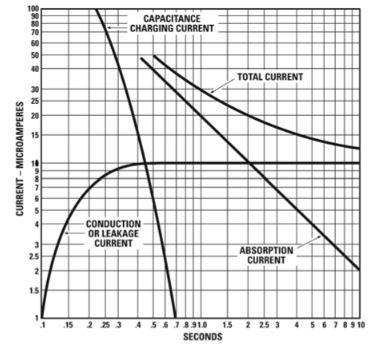
Unlike the dielectric strength test, the value of the voltage to be applied is lower than the insulation level of the element you are measuring. In the case of distribution transformers, this test voltage is usually 5kV, sufficient to generate a conduction current accurately measurable by the measuring device, which many call "Megger"
At DIGAMEL Subestaciones, we offer a complete range of equipment necessary to carry out the dielectric strength test.
Contact us by filling out this form: